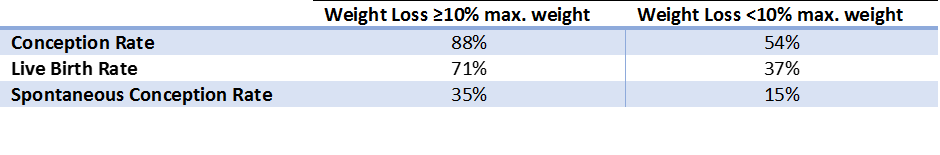|
Being overweight (or more correctly over fat) impacts upon health and importantly fertility. Data shows that overweight women with infertility take longer to conceive, have lower spontaneous conception rates, and have higher rates of infertility treatment cycle cancellation and failure [1]. Males who are overweight or obese have a 50% greater chance of reductions in fertility [2]. If you are male and slightly overweight (average body mass index >25), aerobic exercise (jogging) improves markers of inflammation and oxidative stress that are known to negatively affect sperm [3, 4]. Importantly, for males moderate intensity exercise is superior to high intensity interval training for improving sperm health so you need to get the exercise prescription right. In females with infertility, losing 10% of their maximum weight (eg. losing 7kg if you are 70 kg) through exercise and diet improves rates of conception, live birth rates and spontaneous conception (shown in the table below) [5]. There are so many benefits of eating well and exercising right for fertility besides weight loss though, and there is evidence that engaging in regular physical activity improves the outcome of assisted reproductive treatments, even without substantial weight loss. Being active regularly and eating well improves the outcome of assisted reproductive treatments even in you do not need to loose weight. Get moving and eat to optimise your fertility! Join us for expert advice at The IVF Project. References
1. Luke, B., et al., The effect of increasing obesity on the response to and outcome of assisted reproductive technology: a national study. Fertil Steril, 2011. 96(4): p. 820-5. 2. Sunderam, S., et al., Assisted reproductive technology surveillance--United States, 2006. MMWR Surveill Summ, 2009. 58(5): p. 1-25. 3. Hajizadeh Maleki, B. and B. Tartibian, Moderate aerobic exercise training for improving reproductive function in infertile patients: A randomized controlled trial. Cytokine, 2017. 92: p. 55-67. 4. Hajizadeh Maleki, B., B. Tartibian, and M. Chehrazi, The effects of three different exercise modalities on markers of male reproduction in healthy subjects: a randomized controlled trial. Reproduction, 2017. 153(2): p. 157-174. 5. Kort, J.D., et al., A retrospective cohort study to evaluate the impact of meaningful weight loss on fertility outcomes in an overweight population with infertility. Fertil Steril, 2014. 101(5): p. 1400-3. In response to stress, which may take the form of injury, illness, eating an unhealthy diet, sleep deprivation, other physiological stress or emotional stress, the body’s immune system responds by releasing various chemical regulators in an attempt to restore the normal environment, or ‘homeostasis’. These chemical regulators may be released from the white blood cells of the body which communicate with other cells and tissues. Some of these chemical messengers are small proteins called cytokines which indicate inflammation or activation of the immune system. While acute inflammation is a normal, healthy response to short term stress or injury, chronic low grade inflammation is implicated in a number of disease such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and particularly infertility [1]. Elevated levels of inflammation negatively affect sperm and oocyte quality, reducing fertilisation and conception rate. Reducing inflammation is an effective strategy to enhance fertility, and exercise and diet are proven to reduce inflammation. Having a sedentary lifestyle which includes sitting for long periods of time is associated with higher levels of inflammatory proteins while engaging in regular exercise reduces inflammation. Just as physical activity can modulate inflammation, what you eat can also have an impact. High fat diets increase inflammation while diets high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes reduce inflammation. Exercise can protect against diet induced abnormalities in sperm [2] but a combination of eating a variety of fresh, unprocessed foods and engaging in regular exercise is the ideal way to optimise your fertility. If you do have an occasional meal that would be considered high fat, exercise (the right prescription of aerobic and resistance exercise) beforehand can reduce levels of fats in the blood stream and associated inflammation [3, 4]. In young health males eating fast food exclusively for two weeks, exercise protected against the negative diet induced reductions in good cholesterol (HDL) and insulin resistance [5]. If you plan on eating a high fat meal, head out for a 60 min walk before you indulge to limit the damage! Are you getting the right exercise prescription to optimise your fertility? Do you want to get individualised advice on how to improve your diet for conception? References
1. Maxia N, Uccella S, Ersettigh G, Fantuzzi M, Manganini M, Scozzesi A, et al. Can unexplained infertility be evaluated by a new immunological four biomarkers panel? A pilot study. Minerva Ginecol. 2017. 2. Alhashem F, Alkhateeb M, Sakr H, Alshahrani M, Alsunaidi M, Elrefaey H, et al. Exercise protects against obesity induced semen abnormalities via downregulating stem cell factor, upregulating Ghrelin and normalizing oxidative stress. EXCLI J. 2014;13: 551-572. 3. Fuller KNZ, Summers CM and Valentine RJ. Effect of a single bout of aerobic exercise on high-fat meal-induced inflammation. Metabolism. 2017;71: 144-152. 4. Wilburn JR, Bourquin J, Wysong A and Melby CL. Resistance Exercise Attenuates High-Fructose, High-Fat-Induced Postprandial Lipemia. Nutr Metab Insights. 2015;8: 29-35. 5. Duval C, Rouillier MA, Rabasa-Lhoret R, Karelis AD. High Intensity Exercise: Can It Protect You from A Fast Food Diet? Nutrients. 2017; 9. Dealing with a diagnosis of unexplained infertility can be tough but what is ‘unexplained’ infertility and what does it mean for your chance of conception? Unexplained infertility is defined as the lack of an obvious cause of infertility and failure to achieve a pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected sex, or 6 months in women over the age of 35. In part the diagnosis of unexplained infertility is attributable to the extent and quality of clinical diagnostic tests. The European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology guidelines state that necessary tests should include semen analysis, assessment of ovulation and the luteal phase, and assessment of fallopian tube anatomy (checking your tubes are not closed) by hysterosalpingogram (a procedure using contrast dye and x-ray to view the anatomy of your tubes) or laparoscopy. Can I Conceive with Unexplained Infertility? Spontaneous conception rates in unexplained infertility are actually likely to be higher than couples with a defined cause of infertility. In a review of studies on unexplained infertility it is reassuring that 50% of couples diagnosed with unexplained infertility would conceive spontaneously in the subsequent 12 months, and 12% in the next year [1, 2]. What are Some of the ‘Causes’ of Unexplained Infertility? In studies that have investigated couples with a diagnosis of ‘unexplained infertility’, some of the primary causes have been attributed to poor egg and sperm quality. Sperm DNA fragmentation. This is a major factor in unexplained infertility [3]. There are now recommendations to incorporate testing for sperm DNA fragmentation into routine clinical practice. Sperm is quite susceptible to inflammation and oxidative stress which can damage sperm, causing DNA fragmentation [4]. Inflammation and oxidative stress can be related to diet and not getting the right balance of physical activity and rest. Male factors, such as increased oxidative stress, are also implicated in recurrent pregnancy loss [5]. Assisted reproductive treatments cannot improve DNA fragmentation but there is clear evidence for the effectiveness of reducing DNA damage with the right nutrition and exercise prescription. Elevated Oxidative stress and Inflammation. One study has reported that in females with unexplained infertility, over 70% had high levels of inflammation and oxidative stress [6]. These elevations in inflammation and oxidative stress impact upon oocyte (egg) quality and the endometrium. Altered expression of key proteins in the endometrium are found in infertile women compared to women that have had successful pregnancies suggesting that receptivity of the uterus plays a role in unexplained infertility [7]. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) also have altered expression of receptor proteins in the uterus but lifestyle modifications (through diet and exercise) have been effective at improving receptor levels [8]. Improving Your Chance of Success While IVF and other assisted reproductive treatments will not improve the quality of your eggs and sperm, YOU CAN! You want to give your embryologist the best ingredients possible to work with. Evidence supports that the right exercise prescription and nutrition guidance can improve your chance of success. Want to know where to start? Join us for expert advice and guidance. References
1. Gelbaya TA, Potdar N, Jeve YB and Nardo LG. Definition and epidemiology of unexplained infertility. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2014;69: 109-115. 2. Sadeghi MR. Unexplained infertility, the controversial matter in management of infertile couples. J Reprod Infertil. 2015;16: 1-2. 3. Esteves SC, Agarwal A, Cho CL and Majzoub A. A Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats (SWOT) analysis on the clinical utility of sperm DNA fragmentation testing in specific male infertility scenarios. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6: S734-S760. 4. Tartibian B and Maleki BH. Correlation between seminal oxidative stress biomarkers and antioxidants with sperm DNA damage in elite athletes and recreationally active men. Clin J Sport Med. 2012;22: 132-139. 5. Mohanty G, Swain N, Goswami C, Kar S and Samanta L. Histone retention, protein carbonylation, and lipid peroxidation in spermatozoa: Possible role in recurrent pregnancy loss. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2016;62: 201-212. 6. Maxia N, Uccella S, Ersettigh G, Fantuzzi M, Manganini M, Scozzesi A, et al. Can unexplained infertility be evaluated by a new immunological four biomarkers panel? A pilot study. Minerva Ginecol. 2017. 7. Elnaggar A, Farag AH, Gaber ME, Hafeez MA, Ali MS and Atef AM. AlphaVBeta3 Integrin expression within uterine endometrium in unexplained infertility: a prospective cohort study. BMC Womens Health. 2017;17: 90. 8. Paulson M, Sahlin L and Hirschberg AL. Progesterone Receptors and Proliferation of the Endometrium in Obese Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome-A Lifestyle Intervention Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102: 1244-1253. Stress is associated with adverse IVF outcomes [1] so making a plan to manage your stress is important for both you and pregnancy success. Ensuring you are informed before and during your fertility treatment goes a long way to reducing the stress and anxiety associated with infertility. Treatment awareness, improving lifestyle and understanding how much positive lifestyle change improves treatment outcome can improve your chance of success.
Women with unexplained infertility receiving education and improving lifestyle more than doubled the success of their assisted reproductive treatment (46% pregnancy rate) when compared to a control group who did not receive education and lifestyle change (19% pregnancy rate) [2]. Stay informed and adopt evidence based lifestyle changes that will improve your treatment outcome. What you eat and how much exercise you take part in are two key ingredients that can enhance your fertility. Want to know what you should be doing? Join us at The IVF Project! References 1. Gourounti K, Anagnostopoulos F and Vaslamatzis G. The relation of psychological stress to pregnancy outcome among women undergoing in-vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Women Health. 2011;51: 321-339. 2. Kaya Y, Kizilkaya Beji N, Aydin Y and Hassa H. The effect of health-promoting lifestyle education on the treatment of unexplained female infertility. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016;207: 109-114. Energy balance is the relationship between how much energy you expend through exercise, activities of daily living and your basal metabolic rate (the energy we need to keep our basic bodily functions going), and how much energy you take in from food and drink. For women that have a low body mass index and low body fat levels, engaging in excessive exercise is likely to lead to a negative energy balance unless particular attention is given to ensuring adequate nutrition.
Women with a low body mass index participating in more than 30 minutes per day of moderate or vigorous exercise are at greater risk of anovulation (and hence infertility) (1). Even in normal weight women with no tubal defects and that had never been pregnant, engaging in extremely heavy / vigorous exercise for more than 60 minutes a day increased the risk of ovulatory infertility by 600% (2)! While ensuring you are getting enough nutrients for the amount of activity you are doing is important, so is getting the balance of moderate and vigorous exercise right. It is imperative that your body composition and current activity are considered to prescribe the right amount and intensity of exercise to optimise your menstrual cycle and ovulation. Want to know if your energy balance is supporting conception? Join us today! References 1. Chavarro JE, Rich-Edwards JW, Rosner BA, Willett WC. Diet and lifestyle in the prevention of ovulatory disorder infertility. Obstetrics and gynecology. 2007; 110: 1050-8. 3. Green B, Daling J, Weiss N, Liff J, Koepsell T. Exercise as a risk factor for infertility with ovulatory dysfunction. American Journal of Public Health. 1986; 76: 1432-6. Exercising before your in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment can help to improve your chance of conception. During your treatment though, there may be times you need to modify your physical activity to give yourself the best chance of success. For some women, this will mean doing less, but for other women, this will mean increasing their physical activity levels.
Head over to our friends at FertilitySmarts to find out what you need to know! The bonus is that educating yourself and engaging in lifestyle change can increase the chance of IVF pregnancy by 40%. Food and drug supplements are commonly used by couples looking to improve fertility. There is often the misconception that because a product is labelled as ‘natural’ or formulated to enhance sexual function and fertility, it is safe for conception. Indeed, there are many natural products that have been shown to reduce fertility such as St John’s wort and ginko biloba. There is also the possibility of adulteration of supplements, either intentional of unintentional. Adulteration is when an impure or inferior component not ordinarily part of that substance is found in the supplement. This may be attributable to poor quality manufacturing or the intentional addition of another compound to improve the efficacy of the product, even though this compound may be a pharmaceutical drug with negative effects on fertility. A great example of this is the adulteration of protein powders with anabolic steroids. The steroids are not listed on the label and make the product more effective without any knowledge by the consumer that they are taking steroids, which have negative consequences for fertility. Buyer Beware Be aware of the potential for adulteration, but importantly know the level of scientific evidence that supports the supplements effect on male and female fertility. You may be better placed to ensure your diet is providing you with the optimal levels of micronutrients to boost your fertility. ‘Natural’ is not the same as ‘safe’.
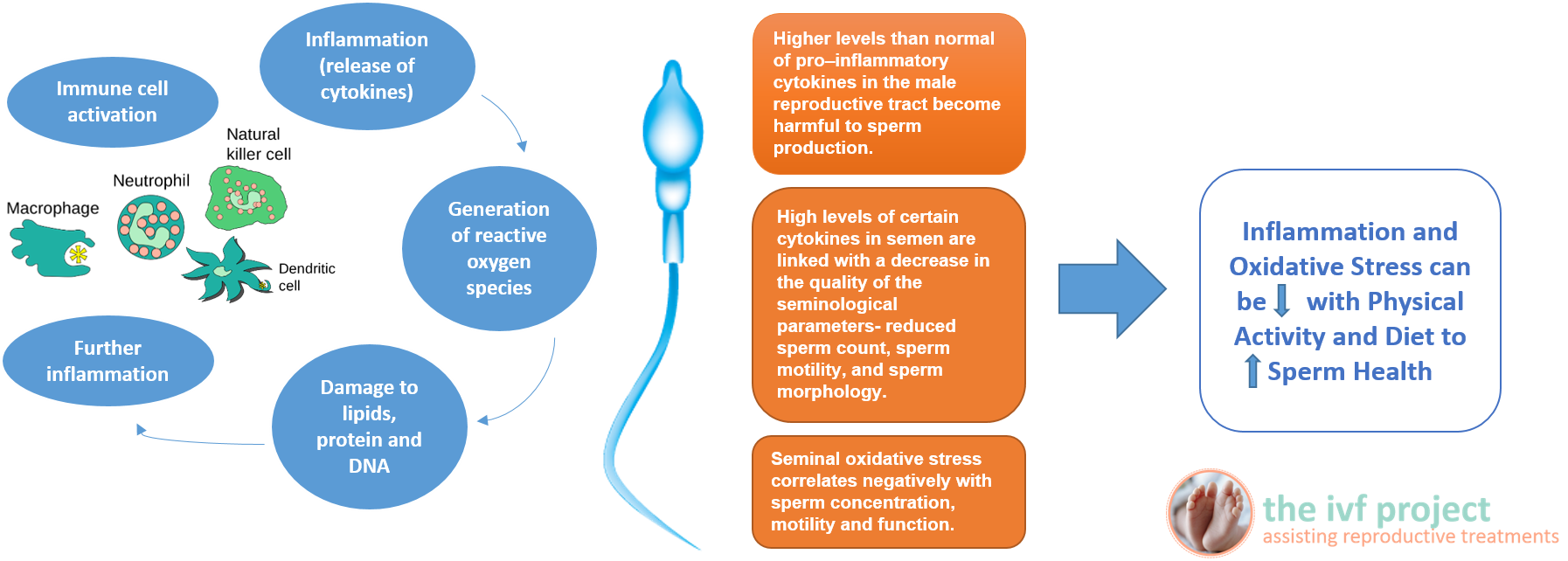
Inflammation is an essential process in tissue repair and immune protection. Inflammation, and the resolution of inflammation, is usually a tightly regulated process but higher than normal levels are related to infertility. Check out our infographic below on inflammation and sperm health. What Causes Inflammation? The cause of higher than normal levels of inflammation are multifactorial. These include a diet missing key micronutrients, carrying excess body fat, hormone imbalances, infections, stress and being sedentary. There is also a link between your gut health and inflammation.
Sperm takes around 80 days to produce and exposure to high levels of inflammation at any point during this period can be harmful to sperm production. Proven strategies to improve sperm health include eating a healthy diet and getting the right amount of exercise. Do you know your intake of key antioxidants for healthy sperm production? Do you have the right exercise prescription? Join us at www.theivfproject.com |
|
1300 084 694
[email protected] Suite T36, 477 Boundary St Spring Hill, Brisbane QLD 4000 Fax. 07 3540 8164 Copyright © 2022
|